No VUS anymore
for CML treatment
We used prime editing to generate and evaluate 97% of all possible single nucleotide variants of ABL1 kinase for resistance to clinically used various TKIs in CML-relevant K562 cells.
Search variants of BCR-ABL1
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML).
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) accounts for 15% of adult leukemias (NCCN, 2021).
CML patients have the BCR-ABL1 fusion, which abnormally activates the kinase function of ABL1.

Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs)
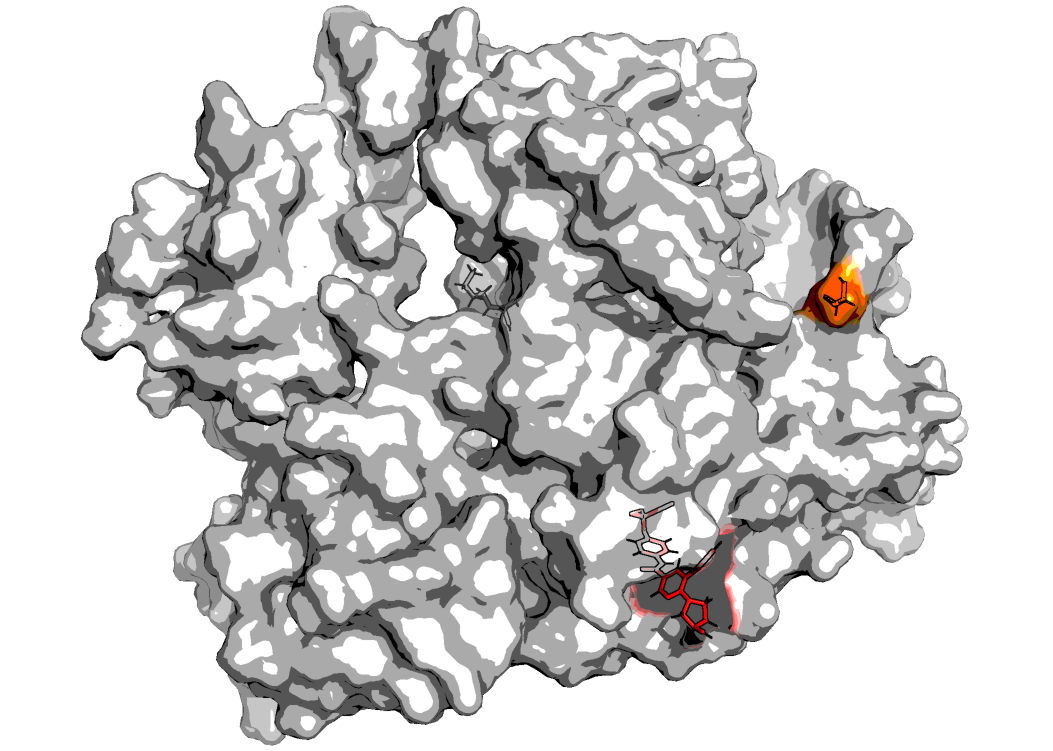
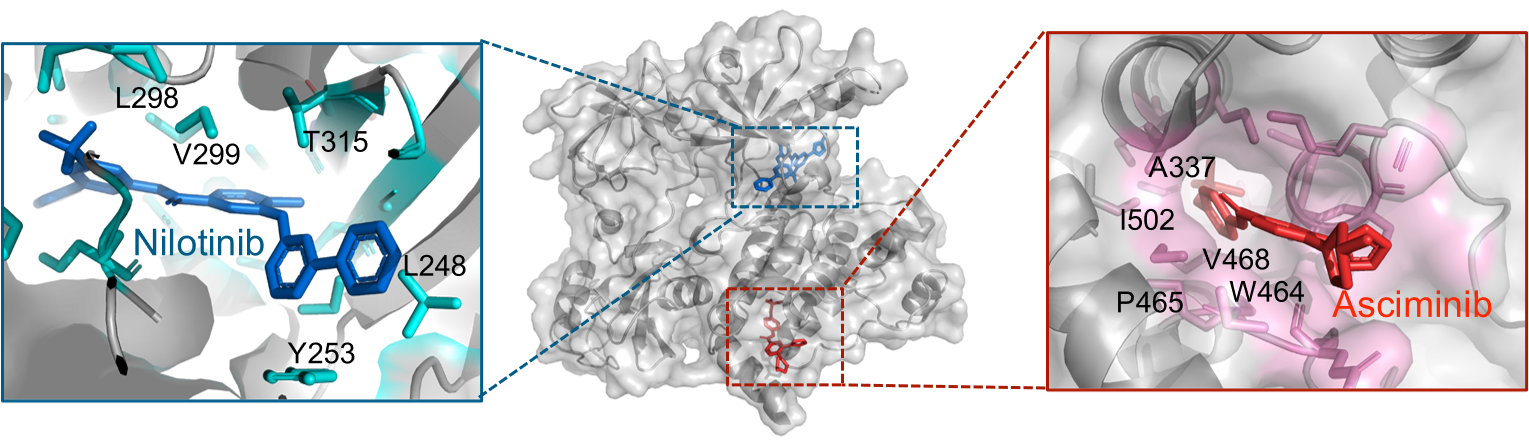
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) such as imatinib have been used to treat CML by inhibiting this abnormally upregulated kinase activity. These TKIs, with the exception of the recently developed asciminib, function by binding to the intracellular ATP-binding pocket of ABL1 in an ATP-competitive manner, thereby preventing ATP from binding and activating the receptor.
However, the majority of ABL1 kinase variants are still categorized as variants of uncertain significance (VUS) with respect to TKI resistance, making it difficult to select appropriate TKIs in patients with given mutations in ABL1.

Saturation genome editing to generate all possible SNVs
To efficiently generate and identify these variants, we designed a total of 8,676 (= 964 bp x 3 substitutions/bp x 3 pegRNAs/substitution) pegRNAs inducing all possible SNVs in the ABL1 kinase.
We induced Saturation Genome Editing (SGE) by independently transducing each library (Exon4, Exon5, through to Exon9) into K562-PE4K cell (K562 cells expressing PE4max with MSH6 knockout) and cultured them for 20 days to induce sufficient prime editing. We further cultured these cell libraries containing the introduced SNVs for an additional 10 days under seven different experimental conditions: the control condition without any treatment, treatment with different TKIs: imatinib, nilotinib, bosutinib, ponatinib, and asciminib.
In line with the fact that the previous results from cell-based assays and clinical studies are sometimes not identical, the functional classifications shown in the current study using cultured cancer cells are also sometimes not identical to the resistance determined in clinical studies as stated above. Thus, the information provided in our study should be used as assisting, not definitive, information for clinical decisions such as TKI selection.